반응형
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1062
1062번: 가르침
첫째 줄에 단어의 개수 N과 K가 주어진다. N은 50보다 작거나 같은 자연수이고, K는 26보다 작거나 같은 자연수 또는 0이다. 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에 남극 언어의 단어가 주어진다. 단어는 영어 소문
www.acmicpc.net
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool alpha[26] = {false, };
vector<string> words;
vector<char> new_alpha;
vector<int> results;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
string word;
cin >> word;
words.push_back(word);
}
alpha['a' - 'a'] = true;
alpha['c' - 'a'] = true;
alpha['i' - 'a'] = true;
alpha['n' - 'a'] = true;
alpha['t' - 'a'] = true;
int cnt = k - 5;
if(cnt < 0){
cout << "0";
return 0;
}
for(string str: words){
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++){
if(alpha[str[i] - 'a'] == false){
new_alpha.push_back(str[i]);
}
}
}
sort(new_alpha.begin(), new_alpha.end());
new_alpha.erase(unique(new_alpha.begin(), new_alpha.end()), new_alpha.end());
vector<bool> v(new_alpha.size(), false);
for(int i = 0; i < cnt; i++){
v[i] = true;
}
do{
vector<int> cn;
for(int i = 0; i < new_alpha.size(); i++){
if(v[i]){
cn.push_back(i);
alpha[new_alpha[i] - 'a'] = true;
}
}
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
bool check = true;
for(int j = 4; j < words[i].size(); j++){
if(alpha[words[i][j] - 'a'] == false){
check = false;
break;
}
}
if(check == true){
sum++;
}
}
results.push_back(sum);
for(int i: cn){
alpha[new_alpha[i] - 'a'] = false;
}
while(!cn.empty()) cn.pop_back();
} while(prev_permutation(v.begin(), v.end()));
cout << *max_element(results.begin(), results.end());
}처음 보았을 때 조합을 이용한 완전 탐색으로 생각하여 바로 풀 수 있었다.
하지만 코드를 너무 의식의 흐름대로 짜서 굉장히 더럽고 벡터를 너무 남발했다는 생각이 들어 다른 블로그들을 참고하여다시 코드를 짜보았다.
완전 탐색 과정에서도 조합이 아닌 재귀함수를 이용한 백트래킹을 통해 더 간결하게 짤 수 있었고
비트마스크를 통해 int 하나에 26개의 알파벳의 배움 유무를 저장할 수 있으며 중복 제거를 따로 해주지 않아도 된다는 장점이 있었다.
결과적으로, 메모리와 시간 관점에서 훨씬 효율적인 코드로 풀이가 가능했다.
// 1062번 백트래킹, 비트마스킹 사용 버전
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int checked;
int word[50]; // n 최대 50
int n, k;
int result;
void func(int toPick, int start){
if(toPick == 0){
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if((word[i] & checked) == word[i]) cnt++;
}
if(result < cnt) result = cnt;
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < 26; i++){
if((checked & (1 << i)) == 0){
checked |= (1 << i);
func(toPick-1, i);
checked &= ~(1 << i);
}
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> k;
string str;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> str;
int num = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < str.length(); j++){
num |= 1 << (str[j] - 'a');
}
word[i] = num;
}
if(k < 5) cout << "0";
else if(k == 26) cout << n;
else{
checked |= (1 << ('a' - 'a'));
checked |= (1 << ('c' - 'a'));
checked |= (1 << ('i' - 'a'));
checked |= (1 << ('n' - 'a'));
checked |= (1 << ('t' - 'a'));
func(k-5, 0);
cout << result;
}
return 0;
}두 코드 수행 시간 비교
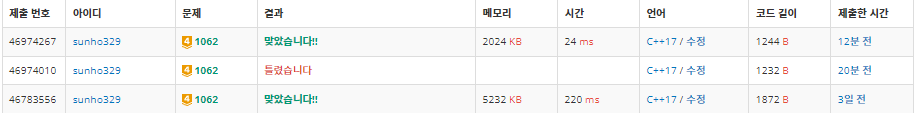
느낀점
다양한 개념을 사용하여 풀 수 있는 문제였다고 생각한다.
비트마스크 알고리즘을 처음 사용해봤는데 효율적인 코드를 위해 알아두면 좋을 것 같다.
반응형
'알고리즘 > BOJ' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BOJ] 4179 - 불! (0) | 2022.07.10 |
|---|---|
| [BOJ] 2580 - 스도쿠 (0) | 2022.07.04 |
| [BOJ] 1339 - 단어 수학 (0) | 2022.07.01 |
| [BOJ] 2941 - 크로아티아 알파벳 (0) | 2022.06.27 |
| [BOJ] 단계별로 풀어보기 - 기본 수학 1 (2) | 2022.06.27 |